
|
|
|---|---|
|
La intervención psicológica en las lesiones deportivas
|
|
|
http://www.efdeportes.com/ Revista Digital - Buenos Aires - Año 8 - N° 52 - Septiembre de 2002 | |
9 / 9
Hongler,R. (1988). El estrés y el miedo en el deporte. Revista de entrenamiento deportivo, 4(2), 20-31.
Hull, C.L. (1933). Hypnosis and suggestibility: An experimental approach. New York: Appleton Century Crofts.
Ievleva, L & Orlick, T. (1991). Mental links to enhanced healing: an exploratory study. Sport psychologist, 5(1), 25-40.
Irwin, R. F. (1975). Relationship between personality and the incidence of injuries to high school football participants. Dissertation Abstracts International, 36, 4328-A.
Jackson, D. W.; Jarrett, H.; Bailey, D.; Kausek, J.; Swanson, M. J. & Powell, J. W. (1978). Injury prediction in the young athlete: A preliminary report. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 6, 6-12.
Jara, P. y Garcés de los Fayos, E. J. (1995). La hipnosis en Psicología del Deporte. Revista de Psicología del Deporte, 7-8, 73-85.
Jaremko, E; Silbert, L & Mann, T. (1981). Differential ability of athletes and non-athletes to cope with 2 types of pain - a radical behavioral-model. Psychological record, 31(2), 265-275.
Johnston, T. (1998). Ted's Turmoil. In B. Rotella, B. A. Boyce, B. Allyson & J. C. Savis, Case Studies in Sport Psychology (pp. 91-94). Sudbury, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
Kamlesh, M.L. (1989). Internal and external factors affecting sport career. Indian Journal of Sport Science.1 (1), 59-67.
Kane, B. (1984). Trainer counseling to avoid three face-saving maneuvers. Athletic training, 19(3), 171-174.
Kanner, A. D.; Coyne, J. C.; Schaefer, C. & Lazarus, R. S. (1981). Comparision of two modes of stress measurement: Daily hassles and uplifts versus major life events. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 4, 1-39.
Kavanagh, D & Hausfeld, S. (1986). Physical performance and self-efficacy under happy and sad moods. Journal of sport psychology, 8(2), 112-123.
Kerr, G. & Minden, H. (1988). Psychological factors related to the occurrence of athletic injuries. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 10(2), 167-173.
Kraus, J. F. & Conroy, C. (1984). Mortality and morbidity from injuries in sports and recreation. Annual Review of Public Health, 5, 163-192.
Krebs, D. E. (1987). Biofeedback in neuromuscular re-education and gait training. In Schwartz, M., Biofeedback. A practitioner's guide. New York: The Guilford Press.
Krebs, D. E. (1988). Biofeedback. In S.B. O'Sullivan; T.J. Schmitz, Physical Rrehabilitation: assesment and treatment, 2,( 629-642). Philadelphia: A. Davis company.
Kroger, W.S. (1963). Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott.
Labrador, F. J. (1987). Técnicas de biofeedback. En J. Mayor y F. J. Labrador, Manual de modificación de conducta (pp.361-398). Madrid: Alhambra Universidad.
Lamas, J.; del Valle-Inclan, F.; Blanco, M. J. y Alcaraz, M. (1985). La escala de grupo de susceptibilidad hipnótica de Harvard (Forma A): Estudio en una muestra española. Análisis y Modificación de Conducta, 11(28), 279-291.
Lamb, M. (1986). Self-concept and injury frequency among female college field hockey players. Athletic Training, 21, 220-224.
Lawlis, J. & Lawlis, G. F.(1990). Health Attribution Test Manual. Champaign, IL: Institute for Personality and Ability Testing.
Lefebvre, B. (1986). La retroaction biologique ou le biofeedback: donnes neuro-psycho-physiologiques actuelles.
Luovain-le-Neuve: Tesis de Doctoral.
Leunes, A. D. & Nation, J. R. (1989). Sport Psychology. An introduction. Chicago. Illinois: Nelson Hall.
Lysens, R., Vanden Auweele, Y., & Ostyn, M. (1986). The relationship between psychosocial factors and athletic injuries. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness,26, 77-89.
Lysens, R.; Auweele, Y. V. & Ostyn, M. (1986). The relationship between psychosocial factors and sports injuries. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 26, 77-84.
Marmer, M.J. (1959). Hypnosis in anesthesiology. Sprinfield: Charles C. Thomas
May, J. R.; Veach, T. L.; Reed, M. W. & Griffey, M. S. (1985). A psychological study of health, injury and performance in athletes on the U.S. alpine ski team. Physician and Sports Medicine, 13, 111-115.
Mcdonald, S. A. & Hardy, CH. J. (1990). Affective Response Patterns of the Injured Athlete: An Exploratory Analysis. The Sport Psychologist, 4, 261-274.
Mcnair, D.; Lorr,M.; Droppleman,L. (1971). Profile of Mood States. Manual. San Diego: Educational and Industrial Testing Service, .
Meyers, M.; Bourgeois, A.; Stewart, S. y Leunes, A. (1991, October). Development and assesment of the sport inventory fon pain. Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Applied Sport Psychology. Savannah, GA.
Miguel Tobal, J. J. y González Ordi, H. (1988). La analgesia hipnótica: un análisis de las principales aportaciones experimentales y clínicas de la hipnosis al tratamiento psicológico del dolor. Revista Española de Terapia del Comportamiento, 6(3), 251-270.
Miller, N.E. (1978). Biofeedback and visual learning. Review of Psychology, 29, 373-404.
Moore, R. A. (1966). Sport and mental health. Springfield, IL: Thomas.
Morgan, W. P. (1993). Hypnosis and Sport Psychology. In J. W. Rhue; J. Lynn, & I. Kirsch, Handbook of Clinical Hypnosis (pp. 649-670). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Morgan, W. P. (1996). Hypnosis in Sport and Exercise Psychology. In J. L. Van Raalte & B. W. Brewer, Exploring Sport and Exercise Psychology (pp. 107-130). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Morrow, J. y Harvey, P. (1990). The exercise salience scale. Unpublished manuscript.
Mueller, D.P., Edwards, D.W., & Yarvis, R.M. (1977). Stressful life events and psychiatric symptomology: Change as undesirability. Journal of Health and Social Behavior,18,307-317.
Navarro-Beltrán, E. (1987). Diccionario Terminológico de Ciencias Médicas. Barcelona: Salvat Editores.
Nideffer, R. M. & Sharpe,R. (1978). A.C.T.: Attention control training. New york: Wyden Books.
Nideffer, R. M. (1993). Attention Control Training. In R. N. Singer, M. Murphey, L. K. Tennant, Handbook of Research on Sport Psychology (pp.542-556). Nueva York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Nideffer, R.M. (1981). The ethics and practice of applied sport psychology. New York.: Mouvement Publications,
Nims, J F. (Ed.)(1983). Western wind: An introduction to poetry (2nd ed.). New York: Random House.
Ogilvie, B. C. & Tutko, T. (1966). Problem athletes and how to handle them. London: Pelham.
Palmi, J. (1983). Una experiencia con bioinformación dentro de la práctica deportiva. Dentro de las jornadas de psicología de la actividad física y el deporte de Cataluña. Barcelona: INEF.
Palmi, J. (1986). La bioinformación como técnica de información directa en el campo de la psicología del deporte. Presentado en el I Congrreso de la actividad física y el deporte. Espluges de Llobregat. INEFC.
Palmi, J. (1987). Biofeedback y registros fisiológicos y una aplicación en el deporte. Comunicación presentada en el II Congreso de la actividad física y el deporte, Granada: INEF.
Palmi, J. (1988). La psicología frente al atleta lesionado. Apunts, 11-12, 24-25.
Palmi, J. (1997). Componentes psicológicos de las lesiones deportivas. En J. Cruz, Psicología del deporte (pp.215-244). Madrid: Síntesis.
Palmi,J. (1987). Tècniques d'autocontrol aplicades a l'esport. IV Jornadas de l'Associació Catalana de Psicología de l'esport. Lleida: INEF.
Palmi,J. (1988). La psicología frente al atleta lesionado. Apunts, 11-12, 24-25.
Palmi,J. y Gordillo, A. (1986). Las tecnicas de biofeedback aplicadas a la actividad física. Apunts d'educació física, 5.
Pargman, D. (Ed.) (1993). Psychological Bases of Sport Injuries. Morgantown: Fitness Information Technology.
Passer, M. W. & Seese, M. D. (1983). Life stress and athletic injury: Examination of positive versus negative events and three moderator variables. Journal of Human Stress, 9(4), 11-16.
Petrie, G. (1993). Injury From the Athlete's Point of View. In J. Heil (Ed.), Psychology of Sport Injury (pp. 17-23). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Petrie, T. A. (1990). Life stress, social support, and injury in woman collegiate gymnasts. Proceedings of the 98th Annual Convention of the American Psychological Association (Abstract), 230.
Raglin, J. S & Morgan, W. P. (1987). Influence of exercise and quiet rest on state anxiety and blood pressure. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 19(5), 456-463.
Rhue, J. W.; Lynn, J. & Kirsch, I. (1993). Handbook of Clinical Hypnosis. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Robbins, J. M & Joseph, P. (1985). Experiencing exercise withdrawal: possible consequences of therapeutic and mastery running. Journal of Sport Psychology, 7(1), 23-39.
Rosemblum, S. (1979). Psychological factors in competitive failures in athletes. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 7, 198-200.
Rotella, J. R. (1990). Atención psicológica al deportista lesionado. En D. N. Kulund, Lesiones del deportista (pp.151-164). Barcelona: Salvat.
Rotella, R. J & Campbell, M. S. (1983). Systematic desensitization: psychological rehabilitation of injured athletes. Athletic training,18(2), 140-142.
Rotella, R. J. y Heyman, S. R. (1991). El estrés, las lesiones y la rehabilitación psicológica de los deportistas. J. M. Williams (Ed.). Psicología Aplicada al deporte. Madrid: Biblioteca Nueva.
Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied, 80 (1), 1-28.
Sanderson, F. H. (1978). Psychological implications of injury. British Journal of sports medicine, 12(1), 41-43.
Sanderson, R. (1977). Psychology of the injury prone athlete. British Journal of Sport Medicine, 11, 56-57.
Sandweiss, J. H.; Wolf, S. L. (1985), Biofeedback and sports science. New York: Plenum Press.
Sarason, I. G.; Johnson, J. H. & Siegle, J. M. (1978). Assesing the impact of life changes: Development of the life experiences survey. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 46(5), 932-946.
Sarason, I. G.; Levine, H. M.; Basham, R. B. & Sarason, B. R. (1983). Assessing social support: The Social Support Questionnaire. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44(1), 127-139.
Schmidt, R. A. (1988). Motor Control and Learning, Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics Publishers.
Schmidt, R.A. (1988). Motor Control and Learning, Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics Publishers.
Selzer, M. L. & Vinokur, A. (1974). Life events, subjective stress, and traffic accidents. American Journal of Psychiatry, 131(8), 903-906.
Shapiro, D. (1982). Generalization and maintenance in biofeedback treatment. In R.B.Stuart, Adherence, compliance and generalization in behavioral medicine,New York.: Brunner/Mazel.
Sheehan, P. W. y Robertson, R. (1996). Imagery and Hypnosis: Trends and Patternings. In R. G. Kunzendorf, N. P. Spanos & B. Wallace, Hypnosis and Imagination (pp. 1-18). New York: Baywood Publishing Company, Inc.
Shor, R. E. & Orne, E. C. (1962). Harvard Group Scale of Hypnotic Susceptibility, Form A. Palo Alto (California): Consulting Psychologist Press.
Shor, R. E. (Ed) & Orne, M. T. (Ed) (1965). Nature of hypnosis: Selected basic readings. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Simon, M. A. (1988). Autoeficacia y tolerancia a la estimulación aversiva: efectos diferenciales del feedback atribucional. Análisis y modificación de conducta, 41(14), 401-417.
Simon, M. A. (1989). Biofeedback y rehabilitación. Valencia: Promolibro,
Simon, M. A. (1991). Biofedback. En V.E. Caballo, Manual de técnicas de terapia y modificación de conducta (pp.373-400). Siglo XXI, Madrid.
Simon, M. A. (1992). Aplicaciones clínicas del biofeedback: revisión crítica de su efectividad en diferentes campos de intervención. En M. A. Simon, Comportamiento y salud (pp.175-218).Valencia: Promolibro.
Simon, M. A. (1992). Aplicaciones clínicas del biofeedback: revisión crítica de su efectividad en diferentes campos de intervención. En M.A.Simon, Comportamiento y salud (pp.175-218).Valencia: Promolibro.
Simon, M. A. y Amenedo, E. (en prensa). Manual de Psicofisiología clínica. Madrid: Ed. Pirámide.
Simón, M. A. y Hernández Mendo, A. (1993, abril). Valoracion de la efectividad de los ejercicios isometricos y del biofeedback-emg en la reeducacion neuromuscular despues de meniscectomia. II Congreso Psicología Conductual (Palma de Mallorca 5 al 7 de abril): Comunicación.
Smith, R. E.; Johnson, J. H. & Sarason, I. G. (1978). Life change, the sensation seeking motive, and psychological distress. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 46(2), 348-349.
Smith, R. E.; Smoll, F. L. & Ptacek, J. T. (1990). Conjunctive moderator variables in vulnerability and resiliency research: Life stress, social support and coping skills, and adolescents sport injuries. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58(2), 360-369.
Smith, R. E; Smoll, F. L & Schutz, R.W. (1990). Measurement and correlates of sport-specific cognitive and somatic trait anxiety: The Sport Anxiety Scale. Anxiety Research, 2(4): 263-280.
Spielberg, C. D. (1966). Anxiety and behavior. New York: Academic Press.
Stuart, J. C. & Brown, B. M. (1981). The relationship of stress and coping ability to incidence of diseases and accidents. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 25(4), 255-260
Swinnen, S. P.; Nicholson, D. E.; Scmidt, R. A.; Shapiro, D. C. (1990). Information feedback for skill acquisition: instantaneous knowledge of results degrades learning. Journal of experimental psychology: learning memory and cognition, 4 (16), 7.
Thomas, R.; Missoum, G.; Rivolier, J. (1987). La psychologie du sport de haut niveau.París: PUF.
Unestáhl, L. A. (1991). Autohipnosis. En J. M. Williams (Ed.), Psicología aplicada al deporte (pp. 413-433). Madrid: Biblioteca Nueva.
Vallejo, M. A. (1984). Consideraciones acerca de las variables activas del entrenamiento en biofeedback en el tratamiento del dolor crónico. Revista Española de Terapia del Comportamiento, 2, 135-158.
Valliant, P. M. (1981). Personality and injury in competitive runners. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 53(1), 251-253.
Vega, M. N. (1990). Biofeedback EMG frontal y terapia cognitiva en el tratamiento de cefaleas tensionales, migrañas y cefaleas mixtas. Análisis y modificación de coducta, 47 (16), 99-120.
Vila, J. (1981). Sistemas psicofisiológicos de respuesta humana. En A. Puerto (ED.), Psicofisiología, 1(pp.55-90). Madrid: UNED.
Wallace, B. & Turosky, D. D. (1996). Imagery, Hypnosis, and Hemispheric Laterality. In R. G. Kunzendorf, N. P. Spanos & B. Wallace, Hypnosis and Imagination (pp. 235-252). New York: Baywood Publishing Company, Inc.
Weiss, M. R & Troxel, R. K. (1986). Psychology of the injured athlete. Athletic training, 21(2), 104-109.
Weitzenhoffer, A. M. (1957). General Techniques of Hypnotism. New York: Grune & Stratton. (Versión en castellano, Técnicas generales de hipnotismo. Buenos Aires: Paidos, 1964).
Weitzenhoffer, A. M.(1989).The practice of hypnotism. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Wiese, D. M; Weiss, M. R & Yukelson, D. P. (1991). Sport psychology in the training room: a survey of athletic trainers. Sport psychologist, 5(1), 15-24.
Wilder, K. C. (1998). The Untimely Collision. In B. Rotella, B. A. Boyce, B. Allyson & J. C. Savis, Case Studies in Sport Psychology (pp. 94-98). Sudbury, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
Williams, J. M. & Roepke, N. (1993). Psychology of Injury and Injury Rehabilitation. In R. N. Singer, M. Murphey & L. K. Tennant, Handbook of Research on Sport Psychology (pp. 815-839). New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Williams, J. M.; Haggert, J.; Tonyman, P. & Wadsworth, W. A. (1986). Life stress and prediction of athletic injuries in volleybal, basketball and cross-country running. In L. E. Unestahl (Ed.), Sport psychology in theory and practice. Orebo, Sweden: Veje.
Williams, J. M.;Tonyman, P. & Wadsworth, W. A. (1986). Relationship of life stress to injury in intercollegiate volleyball. Journal of Human Stress, 12(1): 38-43.
Wilson, V.E. & Bird, E. D. (1981). Effects of relaxation and/or biofeedback trainning upon hip flexion in gymnats. Biofeedback and self-regulation, 6, 25.
Wolberg, L.R. (1948). Medical Hypnosis, Vol.1: The principles of hypnotherapy. New York: Grune & Stratton.
Yaffe, M. (1978). Psychological aspects of sports injuries. Research Papers in Physical Education, 67(3).
Yaffe, M. (1983). Sports injuries. Psychological aspects. British Journal of hospital medicine, 29(3), 224-230.
Young, M. L. & Cohen, D. A. (1979). Self-concepts and injuries among female college tournament basketball players. American Corrective Therapy Journal, 33, 139-142.
Young, M. L. & Cohen, D. A. (1981). Self-concepts and injuries among female high school basketball players. Journal of Sports Medicine, 21, 55-59.
Zaichkowsky,LD.; Fuchs,CZ. (1988). Biofeedback applications in exercise and athletic performance. Exercise Sport Science Revue, 16, 381-421.
Zuckerman, M.; Kolin, E. A. Price, L. & Zoob, I. (1964). Development of a sensation-seeking scale. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 28(6), 477-482.
Anexo22
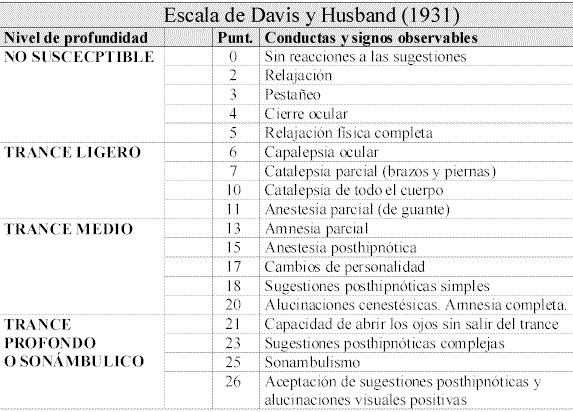
A continuación figura una escala para evaluar la profundidad hipnótica. Existen otras escalas destinadas a este mismo fin, nosotros hemos escogido esta por la claridad del protocolo y la sencillez de su manejo.
Una vez realizado todo el proceso hipnótico, y en función de cómo se haya desarrollado, se marcará con una o varias "X" las categorías que se hayan producido. En el caso de que solo se haya llevado a cabo una de ellas, la puntuación será la asignada a esa categoría. Si se han producido varias, se considerará la de mayor valor.
| Inicio |
sobre Psicología del deporte | Rehabilitación de lesiones
| |
|
|---|---|
|
revista
digital · Año 8 · N° 52 | Buenos Aires, Septiembre 2002 |
|